Cuts
Diamonds are cut in a variety of shapes, such as round, pear, or rectangular. The shape will affect the way a diamond reflects and refracts light, including a stone's sparkle, called brilliance, and the rainbow colors it shows, called dispersion. The shape can also affect how we see the size of the diamond. When choosing a diamond ring, it's important to try on different shapes as each one will look different on the hand.
Shop now
Colors
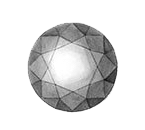
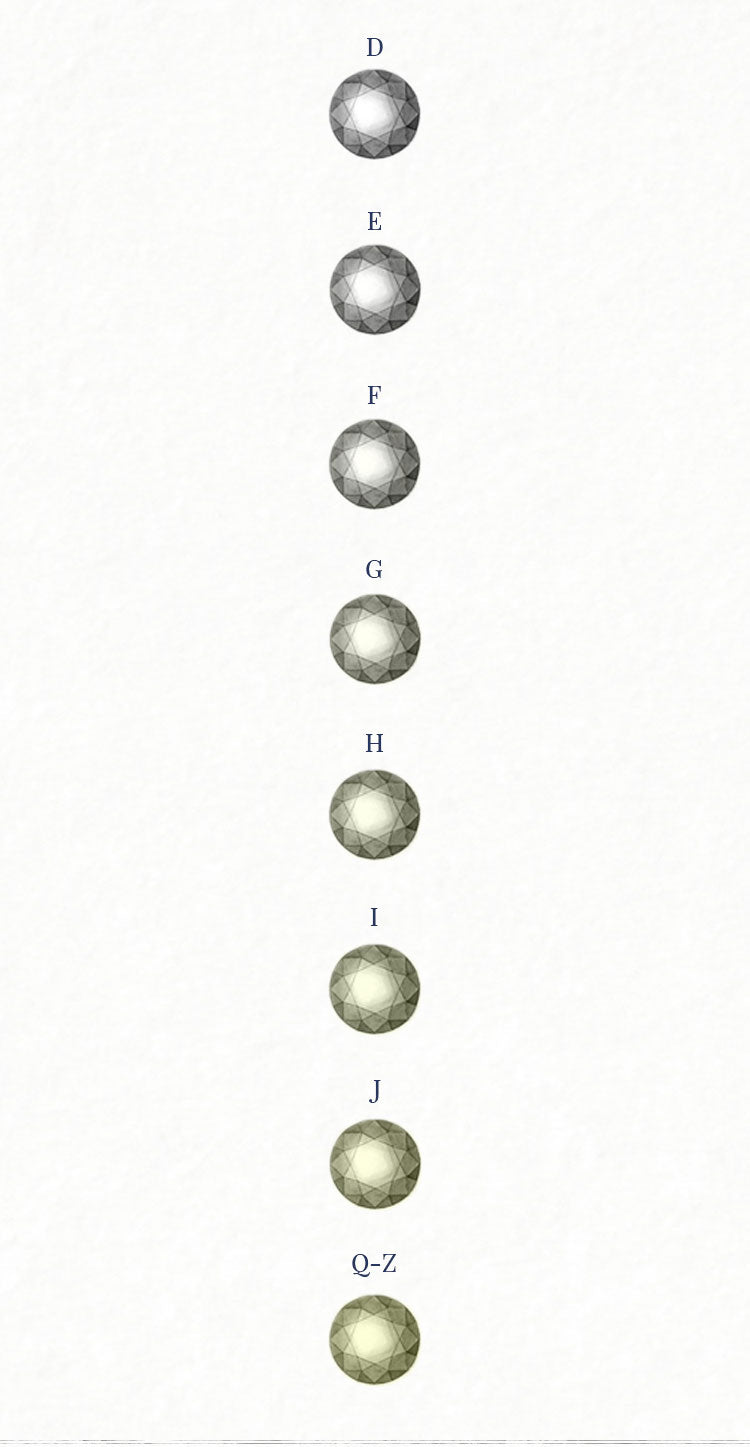
Diamonds naturally come in many different colors, from yellow to pink to blue. The majority are colorless to slightly colored and are graded on the D through Z color scale. D represents a colorless diamond while Z represents a diamond that is significantly colored, typically in shades of yellow or brown. Most diamonds fall somewhere in between, gaining more color saturation as they move further down the alphabet. Diamonds with very saturated color are called Fancy, including Fancy Yellow or Fancy Brown, and are graded on a different color scale. The Fancy color scale measures the stone's hue, tone, and saturation.
Shop now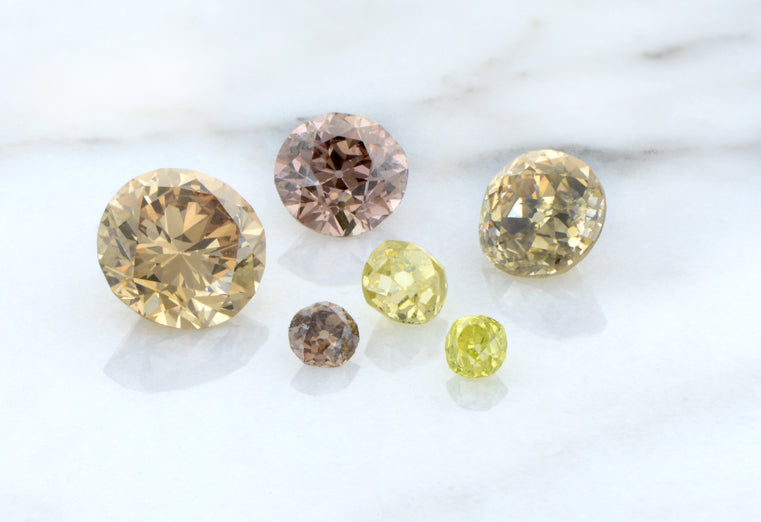
Clarity
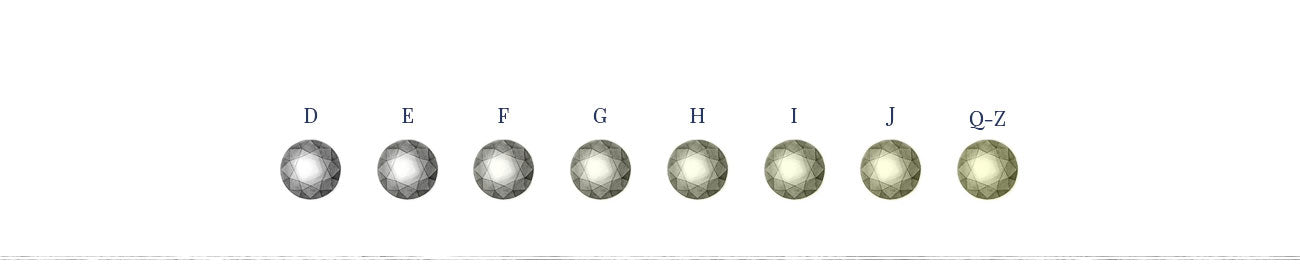
A diamond's clarity is graded based on how visible its clarity characteristics are at 10x magnification. Flawless diamonds have no visible clarity characteristics at 10x magnification, while a Very Very Slightly Included (VVS) clarity diamond has the eqivalent of a pinpoint inclusion. It is difficult even for a trained diamond grader to find VVS inclusions. Clarity characteristics are very small in the Very Slightly Included (VS) grades and become easier to see moving down the clarity scale. At Included (I) clarity, inclusions are visible to the eye without magnification.
Shop now